
ACD/Name (Chemist Version) offers a standardized set of features for quick and simple generation of IUPAC names, and structures from names. It is a streamlined version of our popular ACD/Name software.
View a full description and pricing on our web store.

R-5.6.4.1 Acetals. Compounds with the general structure
 , where R and/or R' may be, but need not be, hydrogen, but
R" and R'" cannot be hydrigen, are termed generically "acetals". "Ketals" constitute a subclass of acetals wherein neither R nor R' may be hydrogen
, where R and/or R' may be, but need not be, hydrogen, but
R" and R'" cannot be hydrigen, are termed generically "acetals". "Ketals" constitute a subclass of acetals wherein neither R nor R' may be hydrogen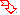 . Acetals
are named substitutively as "alkoxy-", "aryloxy-", etc., derivatives of an appropriate parent hydride or functional parent compound. Alternatively, according to functional class nomenclature, the
name of the appropriate aldehyde or ketone is followed by that of the O-substituent(s), which is in turn followed, after a space, by the word "acetal" or "ketal".
. Acetals
are named substitutively as "alkoxy-", "aryloxy-", etc., derivatives of an appropriate parent hydride or functional parent compound. Alternatively, according to functional class nomenclature, the
name of the appropriate aldehyde or ketone is followed by that of the O-substituent(s), which is in turn followed, after a space, by the word "acetal" or "ketal".
Sulfur analogues of acetals and ketals with the general structuresExamples to R-5.6.4.1
 or
or  , are termed generically "dithioacetals" or "monothioacetals", respectively. They are named
substitutively as "alkylsulfanyl-", "arylsulfanyl-", "alkyloxy-" (or "alkoxy-"), or "aryloxy-", derivatives, as appropriate, of a parent hydride. They may also be named by functional class
nomenclature in the same way as acetals (see above). Capital italic latter locants are used to provide structural specificity. Selenium and tellurium and mixed analogues are treated in the same way
as their sulfur analogues; generically, they are "monoselenoacetals", "ditelluroacetals", "selenothioacetals", etc., and are named substitutively using prefixes such as "alkylselanyl-",
"aryltellanyl-", etc.
, are termed generically "dithioacetals" or "monothioacetals", respectively. They are named
substitutively as "alkylsulfanyl-", "arylsulfanyl-", "alkyloxy-" (or "alkoxy-"), or "aryloxy-", derivatives, as appropriate, of a parent hydride. They may also be named by functional class
nomenclature in the same way as acetals (see above). Capital italic latter locants are used to provide structural specificity. Selenium and tellurium and mixed analogues are treated in the same way
as their sulfur analogues; generically, they are "monoselenoacetals", "ditelluroacetals", "selenothioacetals", etc., and are named substitutively using prefixes such as "alkylselanyl-",
"aryltellanyl-", etc.
R-5.6.4.2 Hemiacetals. Compounds with the general structureExamples to R-5.6.4.1
 are termed generically "hemiacetals"
are termed generically "hemiacetals" . Hemiacetals
are named substitutively as alkoxy-, aryloxy-, etc., derivatives of an appropriate hydroxy parent compound, such as an alcohol (see R-5.5.1.1), and by functional class nomenclature in the
same way as acetals (see R-5.6.4.1) using the class name "hemiacetal".
. Hemiacetals
are named substitutively as alkoxy-, aryloxy-, etc., derivatives of an appropriate hydroxy parent compound, such as an alcohol (see R-5.5.1.1), and by functional class nomenclature in the
same way as acetals (see R-5.6.4.1) using the class name "hemiacetal".
Sulfur analogues of hemiacetals with general structuresExample to R-5.6.4.2
 and
and  or
or  are generically "dithiohemiacetals" or "monothiohemiacetals", respectively. They are
named substitutively as "alkylsulfanyl-", "arylsulfanyl-", "alkyloxy-" (or "alkoxy-"), or "aryloxy-", derivatives, as appropriate, of a hydroxy parent compound, such as an alcohol (see
R-5.5.1.1), or of a thiol parent compound (see R-5.5.1.2). They may also be named by functional class nomenclature in the same way as hemiacetals (see above, R-5.6.4.2).
Selenium and tellurium and mixed analogues are treated in the same way as their sulfur analogues; generically, they are "monoselenohemiacetals", "ditellurohemiacetals", "selenothiohemiacetals", etc.,
and are named substitutively as derivatives of a hydroxy parent compound or a chalcogen analogue, such as a "thiol" or "selenol", using prefixes such as "alkylselanyl-" and "aryltellanyl-", etc.
are generically "dithiohemiacetals" or "monothiohemiacetals", respectively. They are
named substitutively as "alkylsulfanyl-", "arylsulfanyl-", "alkyloxy-" (or "alkoxy-"), or "aryloxy-", derivatives, as appropriate, of a hydroxy parent compound, such as an alcohol (see
R-5.5.1.1), or of a thiol parent compound (see R-5.5.1.2). They may also be named by functional class nomenclature in the same way as hemiacetals (see above, R-5.6.4.2).
Selenium and tellurium and mixed analogues are treated in the same way as their sulfur analogues; generically, they are "monoselenohemiacetals", "ditellurohemiacetals", "selenothiohemiacetals", etc.,
and are named substitutively as derivatives of a hydroxy parent compound or a chalcogen analogue, such as a "thiol" or "selenol", using prefixes such as "alkylselanyl-" and "aryltellanyl-", etc.
R-5.6.4.3 Acylals. Compounds with the general structureExamples to R-5.6.4.2
 ,
,  , etc., are generically called "acylas". Specific compounds are named as esters.
, etc., are generically called "acylas". Specific compounds are named as esters.
Example to R-5.6.4.3
(traditionally Ethylidene dipropionate,
see Note under R-2.5)


Published with permission of the IUPAC by Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc., www.acdlabs.com, +1(416)368-3435 tel, +1(416)368-5596 fax. For comments or suggestions please contact webmaster@acdlabs.com