
ACD/Name (Chemist Version) offers a standardized set of features for quick and simple generation of IUPAC names, and structures from names. It is a streamlined version of our popular ACD/Name software.
View a full description and pricing on our web store.

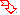 ) are named by
replacing the suffixes "-oic acid", "-ic acid", or "-carboxylic acid" of the name of the acid corresponding to the acyl group by "-amide" or "-carboxamide". The substituent prefix corresponding to
) are named by
replacing the suffixes "-oic acid", "-ic acid", or "-carboxylic acid" of the name of the acid corresponding to the acyl group by "-amide" or "-carboxamide". The substituent prefix corresponding to
 is "carbamoyl-".
is "carbamoyl-".
Some trivial names are retained (see R-9.1, Table 28(a)).Examples to R-5.7.8.1
(see R-5.7.1.2.2)
Substituted primary amides with general structures such as  ,
,  . and the corresponding sulfonamides, are named by citing the substituents R' and R" as prefixes (but
see below for N-phenyl derivatives).
. and the corresponding sulfonamides, are named by citing the substituents R' and R" as prefixes (but
see below for N-phenyl derivatives).
N-Phenyl derivatives of primary amides are called "anilides" and may be named using the suffix "-anilide" in place of the suffix "-amide". Locants for substituents in the N-phenyl ring are primed.Examples to R-5.7.8.1
Alternatively, an N-acyl group may be named as a N-substituent of an amine. This method is used mainly for N-derivatives of nitrogenous heterocycles.Examples to R-5.7.8.1
When a group having preference for citation as a principal characteristic group is present, the groupExample to R-5.7.8.1
 of an N-substituted amide
of an N-substituted amide  may be treated as a substituent of the compound HR'. The group
may be treated as a substituent of the compound HR'. The group  may be expressed as a substituent by changing the "-amide" or "-carboxamide" suffix of the amide name to "amido-" or
"carboxamido-", respectively, or alternatively, by the appropriate "acylamino-" preix.
may be expressed as a substituent by changing the "-amide" or "-carboxamide" suffix of the amide name to "amido-" or
"carboxamido-", respectively, or alternatively, by the appropriate "acylamino-" preix.
R-5.7.8.2 Symmetrical diacyl and triacyl derivatives of ammonia, i.e.,Examples to R-5.7.8.1
 and
and  respectively, are named as di- and triacyl derivatives of
the parent hydride azane, or as di- and triacylamines.
respectively, are named as di- and triacyl derivatives of
the parent hydride azane, or as di- and triacylamines.
The trivial names diacetamide and triacetamide for the compoundsExamples to R-5.7.8.2
 and
and  , respectively, and dibenzamide and tribenzamide for
, respectively, and dibenzamide and tribenzamide for  and
and  ,
respectively, have been used but are not included in these recommendations for use in naming carbon-substituted derivatives.
,
respectively, have been used but are not included in these recommendations for use in naming carbon-substituted derivatives.
Unsymmetrical di- and triacyl derivatives of ammonia, such as  ,
,  , and
, and  , may be named (a) on the basis of the parent
hydride azane; (b) as a diacylamine, a diacylalkyl- (or aryl, etc.) amine, or a triacylamine; or (c) as alkyl (or aryl, etc.) or acyl derivatives of a primary amide (see R-5.7.8.1),
diacetamide, or dibenzamide.
, may be named (a) on the basis of the parent
hydride azane; (b) as a diacylamine, a diacylalkyl- (or aryl, etc.) amine, or a triacylamine; or (c) as alkyl (or aryl, etc.) or acyl derivatives of a primary amide (see R-5.7.8.1),
diacetamide, or dibenzamide.
R-5.7.8.3 Imides are compounds containing the structural groupingExamples to R-5.7.8.2
 and may be considered as nitrogen analogues of anhydrides or as diacyl derivatives of
ammonia. Acyclic imides are named according to R-5.7.8.2. Cyclic imides are named by replacing the suffixes "-dioic acid", "-ic acid", or "-dicarboxylic acid" of the corresponding dibasic
acid by "-imide" or "-dicarboximide". They can also be named as heterocycles.
and may be considered as nitrogen analogues of anhydrides or as diacyl derivatives of
ammonia. Acyclic imides are named according to R-5.7.8.2. Cyclic imides are named by replacing the suffixes "-dioic acid", "-ic acid", or "-dicarboxylic acid" of the corresponding dibasic
acid by "-imide" or "-dicarboximide". They can also be named as heterocycles.
R-5.7.8.4 Hydrazides. Monoacyl derivatives of the parent hydride diazane (hydrazine),Examples to R-5.7.8.3
 , have the generic name "hydrazides" and are named by replacing the
"-ic acid" or "-oic acid" suffix of the name of the acid by "-ohydrazide" or the suffix "-carboxylic acid" by "-carbohydrazide".
, have the generic name "hydrazides" and are named by replacing the
"-ic acid" or "-oic acid" suffix of the name of the acid by "-ohydrazide" or the suffix "-carboxylic acid" by "-carbohydrazide".
Alkyl, aryl, cycloalkyl, etc., substituents on the nitrogen atoms of hydrazides are described by the appropriate prefix names using the locants N- (or 1'-) for the imino nitrogen atom and N'- (or 2'-) for the amino nitrogen atom. Hydrazide derivatives may also be named as derivatives of the parent hydride diazane (hydrazine).Examples to R-5.7.8.4
Diacyl, triacyl and tetraacyl derivatives of hydrazides are named on the basis of the parent hydride diazane (hydrazine).Examples to R-5.7.8.4
When a group having priority for citation as a principal characteristic group is present, a hydrazide group is expressed by the prefix "acyldiazanyl-" (acylhydrazino-). Locants for positions on the hydrazino- group are N- (or 1-) for the nitrogen atom adjacent to the free valence position and N'- (or 2-) for the other nitrogen atom.Examples to R-5.7.8.4
Examples to R-5.7.8.4


Published with permission of the IUPAC by Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc., www.acdlabs.com, +1(416)368-3435 tel, +1(416)368-5596 fax. For comments or suggestions please contact webmaster@acdlabs.com