
ACD/Name (Chemist Version) offers a standardized set of features for quick and simple generation of IUPAC names, and structures from names. It is a streamlined version of our popular ACD/Name software.
View a full description and pricing on our web store.

212.2 - An oxygen atom directly attached to two carbon atoms already forming part of a ring system or to two carbon atoms of a chain may be indicated by the prefix "epoxy-", particularly when it is desired to preserve the name of a specific complex structure, as, for example, steroids or carotenoids. (see also Rule B-15).Examples to Rule C-212.1
212.3 - Compounds RO-X-OR, where the two parent compounds RH are identical and contain a group having priority over ether for citation as suffix, and -X- is any bivalent radical, are named by the method for assemblies of identical units (Subsection C-0.7).Examples to Rule C-212.2

[see Rule C-16.11(examples), (a) (viii)]
or 1,3-Epoxy-2-methylhexane
[see Rule C-16.11(examples), (b) (ii) ]
[Note: epoxy is not alphabetized;
see Rule C-16.11(examples), (a) (viii)].
212.4 - Linear polyethers derived from three or more molecules of aliphatic dihydroxy compounds are most conveniently named by the openchain replacement nomenclature (see Subsection C-0.6).Example to Rule C-212.3
212.5 - Symmetrical linear polyethers may be named in terms of the central oxygen atom when there is an odd number of ether oxygen atoms. or in terms of the central hydrocarbon group when there is an even number of ether oxygen atoms.Examples to Rule C-212.4
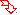
Examples to Rule C-212.5
See Recommendations'93 R-5.5.4


Published with permission of the IUPAC by Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc., www.acdlabs.com, +1(416)368-3435 tel, +1(416)368-5596 fax. For comments or suggestions please contact webmaster@acdlabs.com