
ACD/Name (Chemist Version) offers a standardized set of features for quick and simple generation of IUPAC names, and structures from names. It is a streamlined version of our popular ACD/Name software.
View a full description and pricing on our web store.

R-9.2.1.1 An acyclic bridge is named as a prefix derived from the hydrocarbon name by changing the final "e" to "o". The locant of a double bond, is present, is indicated in square brackets between the hydrocarbon prefix and the ending "-eno", "-dieno", etc.
R-9.2.1.2 A monocyclic hydrocarbon bridgeother than benzene is named by the same prefix as used as a fusion prefix (see R-2.4.1) preceded by "epi-".Examples to R-9.2.1.1
Methano Ethano Propano Butano Etheno Prop[1]eno But[1]eno But[2]eno But[1,3]dieno
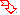 The bridge is assumed to have the maximum number of noncumulative double bonds consistent with the attachment to the fused ring and/or to other
bridges. The positions of the free valences are indicated by the relevant locants in square brackets directly in front of the bridge name.
The bridge is assumed to have the maximum number of noncumulative double bonds consistent with the attachment to the fused ring and/or to other
bridges. The positions of the free valences are indicated by the relevant locants in square brackets directly in front of the bridge name.
R-9.2.1.3 Other cyclic hydrocarbon bridgeare named by prefixes derived from the unsaturated hydrocarbon name (see Table 20). Locants enclosed in square brackets are used as needed.Examples to R-9.2.1.2
R-9.2.1.4 An acyclic heteroatomic bridgeis named by the appropriate prefixExamples to R-9.2.1.3
 .
.
R-9.2.1.5 Heterocyclic bridgesare named by prefixes derived from the corresponding heterocyclic compound name (see Table 23). Locants enclosed in square brackets are used where necessary.Examples to R-9.2.1.4
Epoxy Epithio Episeleno Epidioxy Epidithio Epoxythio Epoxythioxy Epoxyimino Epimino Diazano Diazeno Triaz[1]eno Phosphano Stannano Epoxymethano Epoxyethano Epoxyprop[1]eno
Examples to R-9.2.1.5
[3,4]Furano


Published with permission of the IUPAC by Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc., www.acdlabs.com, +1(416)368-3435 tel, +1(416)368-5596 fax. For comments or suggestions please contact webmaster@acdlabs.com